The first stage of the project focuses on assessing whether a Van de Graaff generator (VDG) can produce field strengths sufficient to contribute to CO₂ bond disruption.
Key objectives:
- Measure maximum achievable voltage
- Evaluate stability and discharge behavior
- Quantify energy throughput
- Assess feasibility for CO₂ excitation and plasma formation
To ensure accuracy and safety, our team is in the process of constructing a liquid high-voltage divider, enabling measurement of multi-hundred-kilovolt potentials.
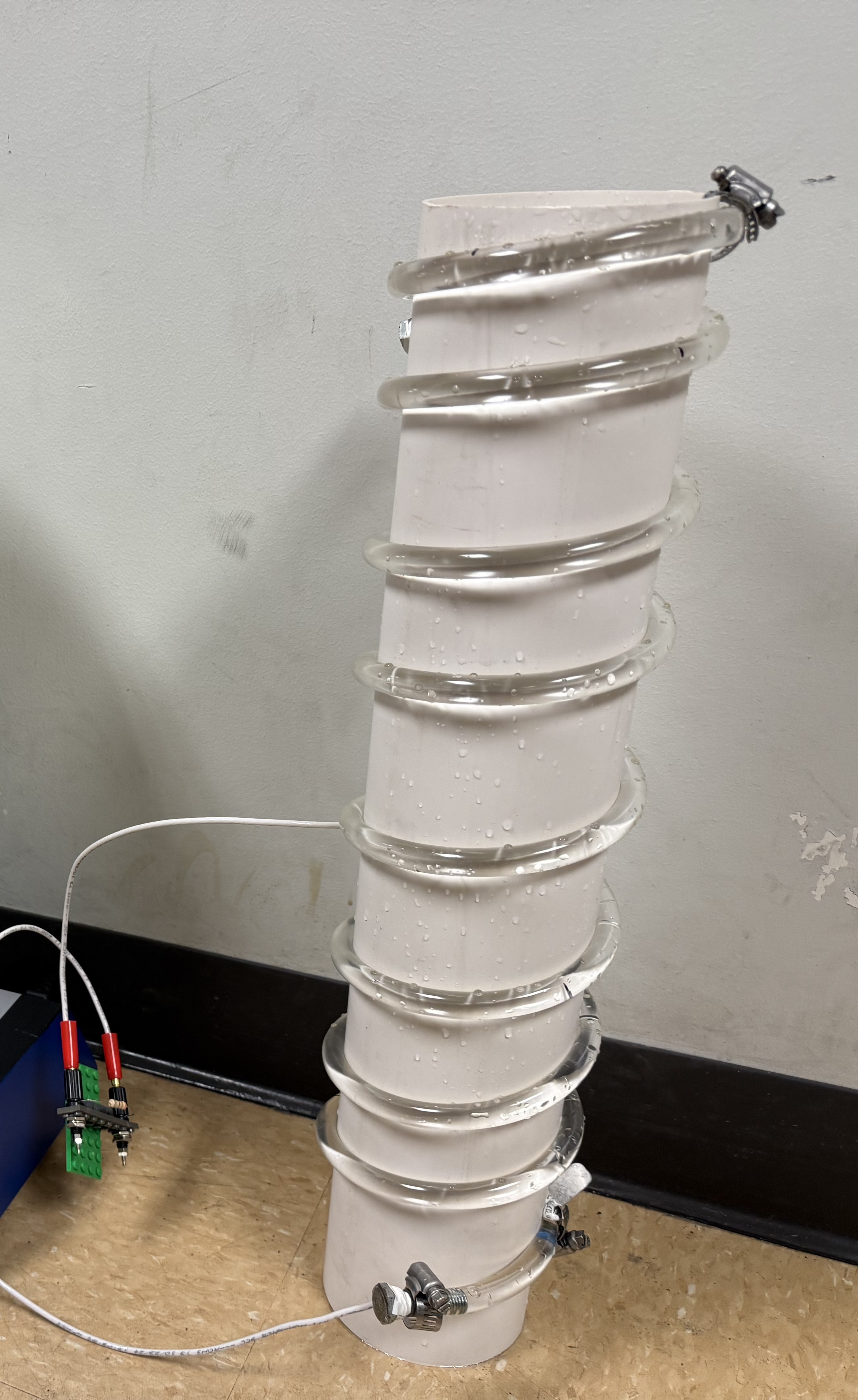

Preliminary analysis and prior NAU work indicate that open-air VDG operation is not sufficient for meaningful CO₂ dissociation:
- VDGs provide high voltage but very low current, limiting energy per pulse.
- Open-air discharges result in negligible dissociation due to low energy density.
- Dissociation products rapidly recombine without temperature and pressure control.
- Past NAU Car Filter teams reported no measurable CO₂ conversion under atmospheric conditions.
These findings motivate the transition to Phase II, where environmental control becomes central.
The core of Phase II is a modular, heatable, pressure-regulated reaction chamber designed to address the limitations of open-air discharges.
Planned capabilities include:
- High-temperature operation to reduce required bond-breaking energy
- Adjustable pressure to study Paschen behavior and plasma stability
- Interchangeable and adjustable electrodes for rapid testing of power-delivery methods
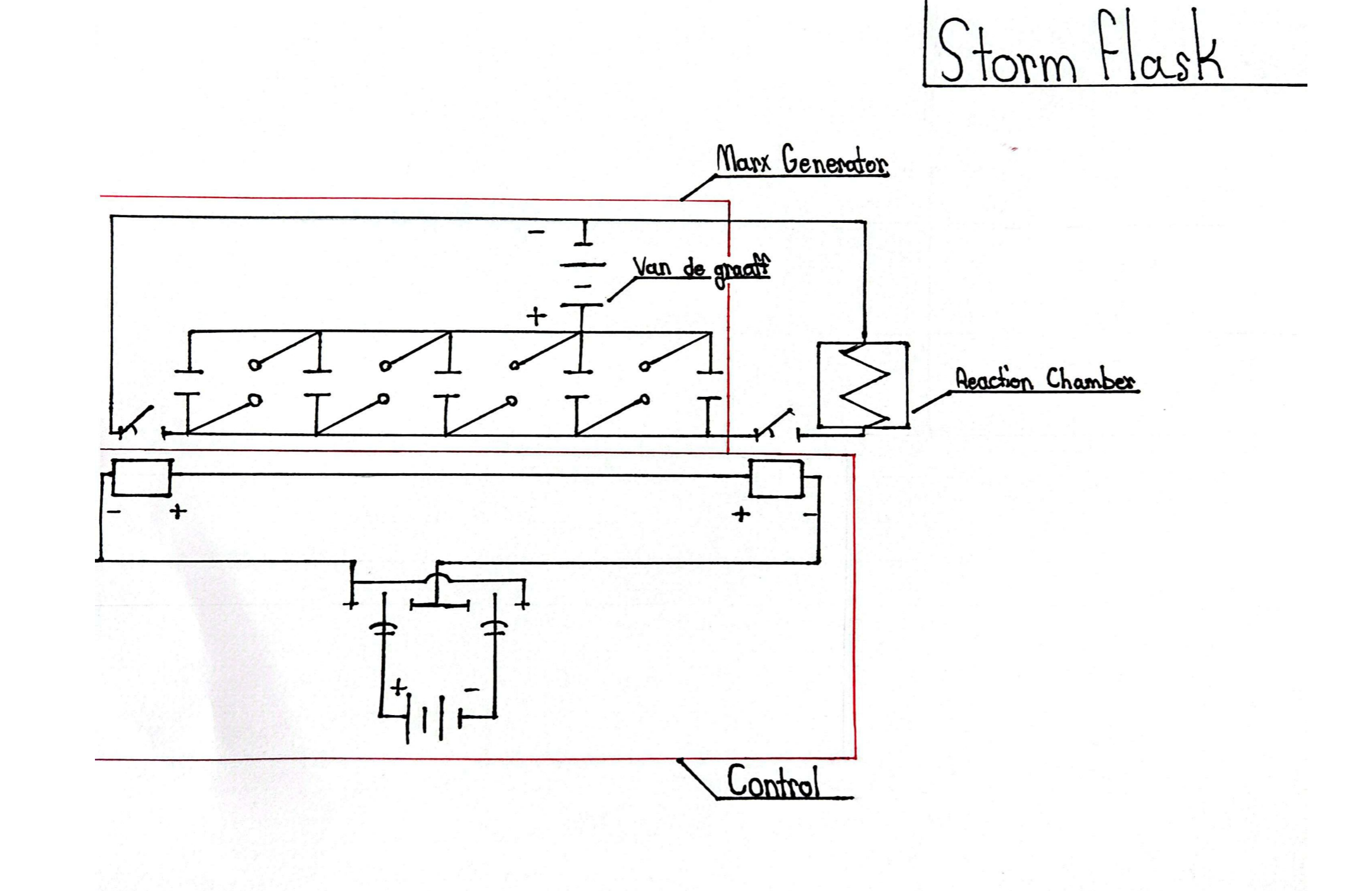
- Modularity for future integration of Marx generators, RF or microwave excitation, and higher-current pulsed systems
- Optical access for spectroscopy and plasma diagnostics (future capability)
This system enables direct investigation of thermally assisted and plasma-enhanced CO₂ dissociation under controlled conditions.
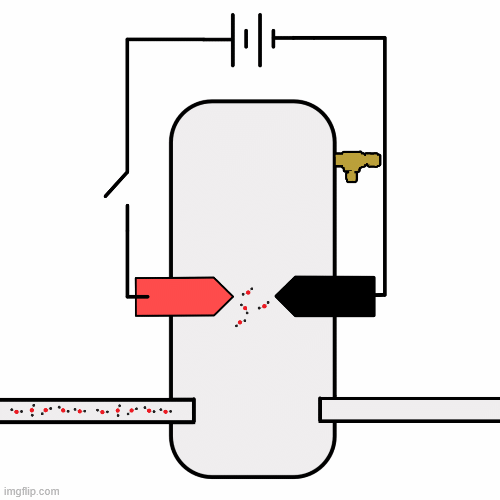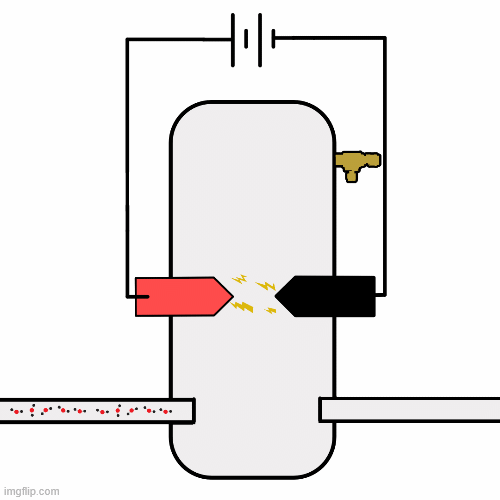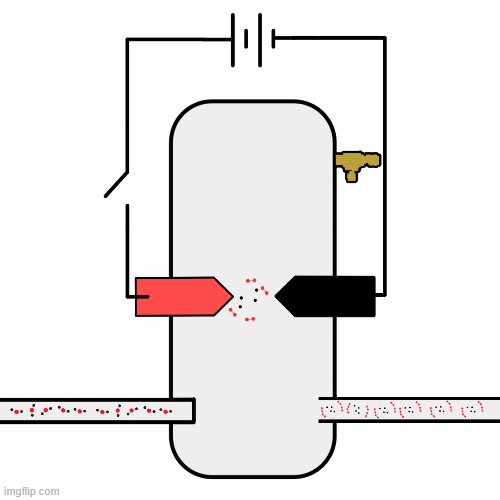
Visuals help communicate how the system is arranged and what physics it targets. As more data and models become available, this section can grow with additional images.
Standards, Safety & Compliance
The experimental design follows established engineering and laboratory safety standards, including:
- OSHA 29 CFR 1910.333 – Electrical safety and work practices
- OSHA 1910.104 – Pressurized and compressed gases
- IEEE 510 – Safety in high-voltage and high-power test areas
- IEEE 433 – High-voltage measurement techniques
- ANSI Z535 – Hazard signage and communication
- ASME BPVC Section VIII – Pressure-vessel considerations
- ASTM dielectric and insulation standards (e.g., D149, D150, D257)
All high-voltage testing will be performed in a restricted-access, grounded, shielded environment with appropriate PPE, interlocks, and documented procedures.
 Phase I: Van de Graaff High-Voltage Evaluation
Phase I: Van de Graaff High-Voltage Evaluation
 Limitations of Open-Air VDG Dissociation
Limitations of Open-Air VDG Dissociation
 Phase II: Controlled CO₂ Reaction Chamber
Phase II: Controlled CO₂ Reaction Chamber
 Experiment Diagrams & Formulas
Experiment Diagrams & Formulas
 Standards-Based Safety
Standards-Based Safety