Problem Definition
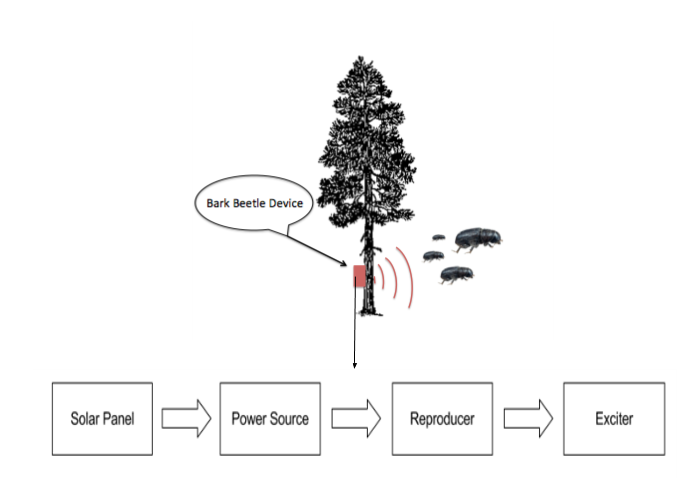
A bark beetle is an insect that creates tunnels by chewing the outermost layer of the tree, also known as the bark of the tree. Once the beetles reach the nutritious inner bark, they emit pheromones to attract other bark beetles. The insect then reproduces and stores the eggs between the bark and the wood. By doing so, the beetles infest the tree not only with bark beetles, but they also carry a blue-stain fungus, which prevent nutrients to flow, accelerating the death of the tree.
The invasive nature of bark beetles is financially detrimental to homeowners, national parks and tree owners. A solution is to use the bark beetle's own sounds to prevent them from occupying the tree. Our sponsor, Dr. Hofstetter, has developed an audio signal that is incompatible to bark beetles sane behavior, interrupting their communications, which prevents them from infiltrating a tree. When the signal is introduced to a tree that has already been occupied, it successfully forces the beetles to evacuate the tree.
The technology Dr. Hofstetter is currently using is cumbersome and uses more power than necessary for the consumer. The objective of this project is to design and successfully optimize the size, energy efficiency, and cost while designing it to be aesthetically and ordinarily pleasing. This final design has a low impact cost to the consumer and the lowest power draw at a reasonable cost from the materials. In the future, this device can have implementations of 'smart' technology. This includes monitoring, wireless connectivity, and automatic control features. These additions can further widen its uses to other geo-locations and species for consumers, businesses and industries.
Research Survey
A. Raspberry Pi

After the second meeting with our clients, our team discovered that the device should broadcast at a minimum of 13 kHz frequency for the audio signal. However, the previous sound module cannot reconstruct high frequencies for the audio signal. Moreover, the power source can be unstable, potentially causing a fire and/or exploding when the battery is overcharged. From the reasons mentioned above, a microcontroller or microprocessor is required for our project. Several versions of micro controllers exist in the market and the popular models include the TI MSP430 and the Arduino Uno. Nevertheless, such microcontrollers do not have a built-in audio output on board which would limit the capabilities for the project. Also, these microcontrollers require extra storage such as a SD card to store audio files. Considering the convenience and budget, Raspberry Pi is the best choice to use.
B. HDMI interface

High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary interface for audio and video data transmission. In the previous research, the sound module has a standard audio output which does not reproduce high-frequencies. In order to have the highest possible audio frequency, we looked into several interfaces and electrical components which enabled ultrasonic acoustic signals. Then, we discovered that HDMI interfaces inherit this feature of up to 192 kHz of PCM audio, which satisfies the project's requirements. Therefore, the device would be able to transmit high-frequency audio signals without aliasing.
C. Tweeter

Due to the changes in the initial parameters of the project, the client requested the device to be capable of reproducing ultrasonic frequencies, up to 100 KHz. Since the limitation of the excitation frequency response is limited to 20 KHz, further research had to be conducted on different audio inducers. Tweeters are a special type of loudspeakers capable of producing higher frequencies from 2 KHz to 25 KHz. Also, there are specialty tweeters, that can reach up to 100 KHz, but are costly. These tweeters operate like conventional loudspeakers, using voice coils suspended within a fixed magnetic field. There are different type of tweeters available, but we mainly focused on the Ribbon and the Super tweeter. The frequency response on the round ribbon tweeter ranged from 2.5 KHz to 40 KHz, however, the super tweeter has a frequency response of up to 50 KHz. The super tweeter requires more power to operate than the ribbon tweeter.
D. Exciter Transducer Technology
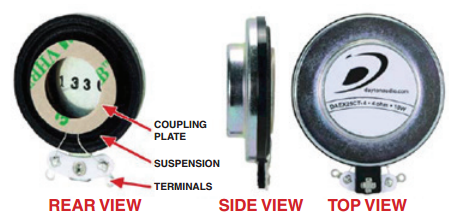
The exciter will be considered as an alternative audio loudspeaker for the device if the power consumption of the tweeter is becomes too high. An exciter transducer is similar to a conventional speaker, instead of the speaker using a vibrating cone to produce the sound, the exciter vibrates at a single point in a chaotic manner as longitudinal sound waves reproducing the sound along a planar surface. The main components in an exciter; are the motor assembly, voice coil, suspension system and electrical connection terminals. The type of surface material the exciter is placed on and where will it be placed, will have sufficient sound being produced. The power consumed by the exciter goes up with an increase in sound performance. To keep the device energy efficient, our team will be limited to using minimal power possible. In a research conducted by Dublon and Portocarrerro, titled "Listentree: Audio-Haptic Display in the Natural Environment", they were able to produce audio sound from a tree in its natural environment. To create this effect, they attached an exciter transducer at the base of a tree trunk underground. With the exciter connected to an audio device the exciter emits the sound throughout the tree enabling the tree to become a speaker. Using this method along with Dr. Hofstetter's approach, we will be able to reproduce the audio files provided for the operations towards the tree.
E. Battery Categories

In this section, we considered the different types of rechargeable batteries available to determine the ideal option for this project. The team is considering six different type of batteries: Nickel Cadmium, Nickel Metal Hydride, Lithium Ion, Lead Acid, and general deep cycle batteries. Nickel Cadmium batteries have a low internal resistance, which implies that it can provide a high current rate and charge rapidly. It's also known that these batteries have the potential to be detrimental for the environment because Nickel Cadmium batteries are toxic. The Nickel Metal Hydride batteries are considered to have a higher energy density per volume and weight compared to the Nickel Cadmium. Lithium Ion batteries have a higher voltage capacity and is in the range from 3 to 4.2 volts. These batteries have a low discharge rate which will help with stabilizing the power in the device. The small sealed lead acid batteries are also known as maintenance-free batteries, which does not meet our project requirements because a full discharge causes extra strain and each cycle decreases the battery life. This battery also has the lowest energy density compared to the nickel-based batteries. Deep Cycle batteries have the characteristics to be ideal for renewable energy due to long period power duration and slow discharge rate. They have the capacity to store large amount of energy in a single battery.
F. Frequency Approach
The problems bark beetles creates is well documented and their paths of destruction is well-known to researchers and various teams dedicated to finding a solution for infested forests. Despite the volumes of papers published over the years with potential solutions, there has yet been a system and/or technology not put in place, for a practical method for the eradication and removal of the invasive bark beetle. Our group will investigate certain aspects of the behavior of bark beetles to find potential weak areas for the most effective solution using a frequency/signal based approach on the client's previous work. The foundation has been laid for a system by the early developments from our client, Dr. Hofstetter, using frequency analysis and audio exciters. The essence of the client's work has been the audio recordings of bark beetles in a synthetic environment and the results being recorded and replayed for any possible effects on their behavior. This fundamental area of using bark beetle sounds as a weapon may have profound consequences in combating any invasive species of bark beetle. The client has stated that more research needs to be done in this area, as the delivery system of using audio exciters needs to be explored. Now this idea will be explored with the use of Super Tweeters due to the client's changes of using a system that could go beyond the 15 kHz limitation of the the audio exciter. The full spectrum of capabilities, limitations, and functionalities of this unique system needs to be made, as well as the fine tuning of the hardware and software aspects of the audio exciters for maximum effectiveness.
G. Beetle Behavior
In order to have a successful and targeted approach to deter and control Dendroctonus Ponderosae (beetle) infestations in trees, research must be focused on the behavior and environment dynamics. There have been extensive tests on these species based on the chemical, biological, and behavioral methods in order to have effective results. Yet, none has been successful enough to control or suppress the spread of beetle reproduction effectively around forests. Of the simplest methods, chemicals and insecticides have been the method of common use. The realistic effects of population reduction of bark beetle infestation of non-infected trees are possible only with highly elevated methods of control. These methods include doses, application methods, combination of chemicals/insecticides, and side-effects of other insects and animals that are essential to the health of the tree and forest. These unintentional side-effects and elevated warnings of heavy chemical use have in most cases become complicated and dangerous for industrial applications in large. In addition, most states are regulated by the EPA and require permission throughout states and national forests. However, they are typically used in reduced, targeted trees for commercial and private use.
Behavioral control has been another method for potential use in controlling bark beetles, to affect reproduction and mate attraction by artificial means to divert any future infestations of the desired tree(s). More specifically, pheromone manipulation to attract the beetles towards traps. The main components in beetle pheromones, frontalin and ipsdienol, are key factors for attraction. Other methods that are effective but undesired include the salvaging of trees and cutting down the infected trees to prevent further spread beetle infiltration. As it is known that once eggs are infused under the bark, it is essentially considered an infected tree. After a year, discoloration starts to become visible. This method is only viable when there are no shortage of trees, and the area infected is targeted and closed by section of an infected forest. Any surrounding trees that are invisibly infected is the problem, the affected area will eventually continue to spread. For these reasons, it is why our efforts have been inclined towards audible, sensory and receptacle research as a way to artificially manipulate beetle infiltration in forests.
Design Concept
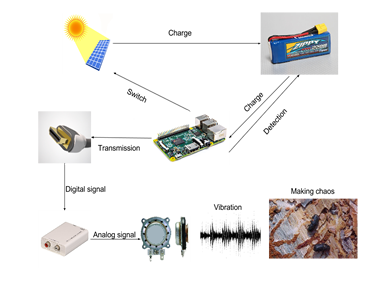
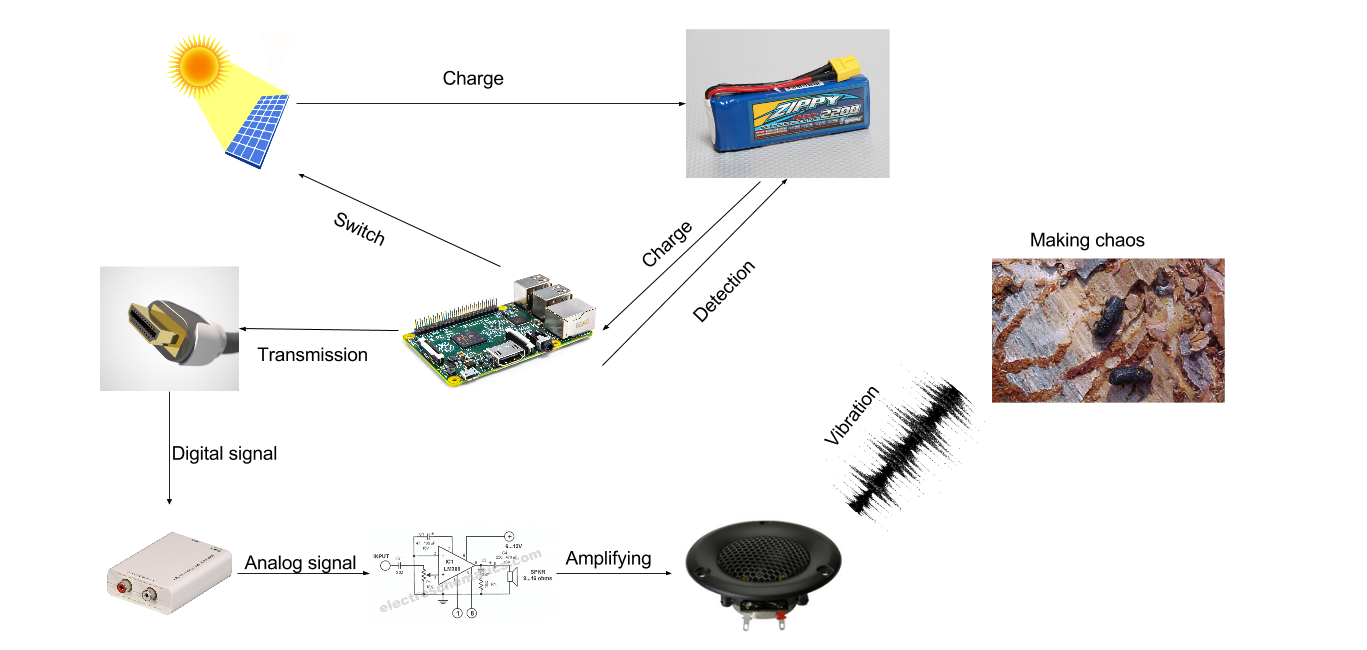
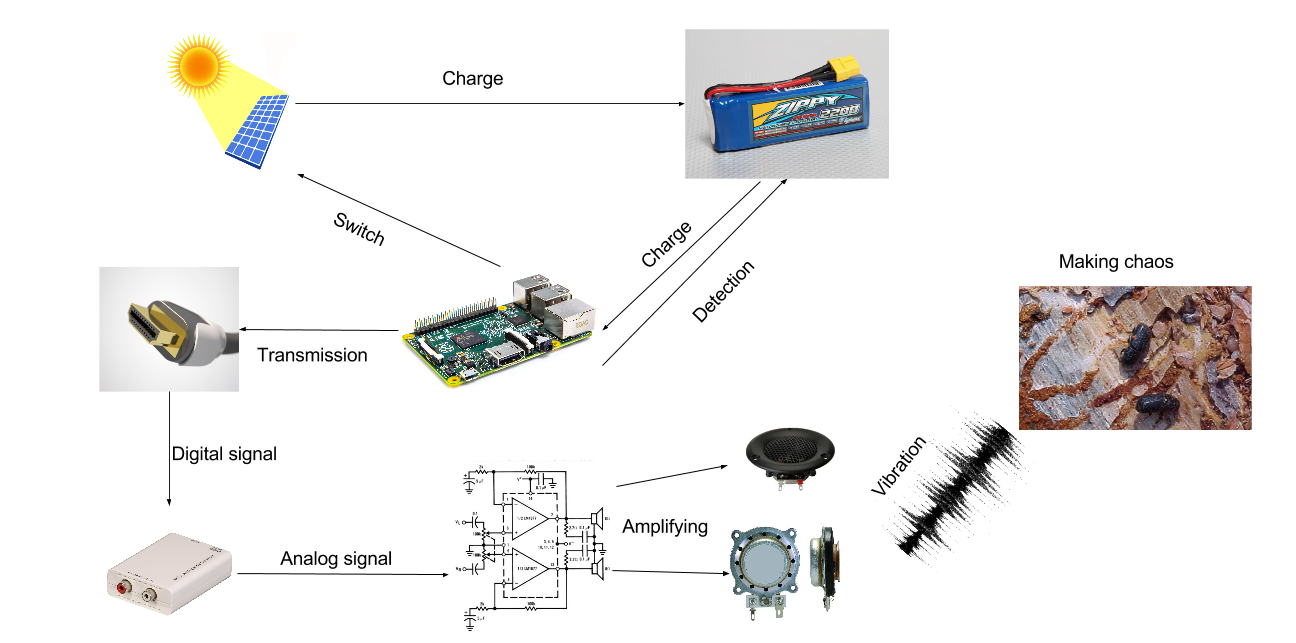
System Flow Chart
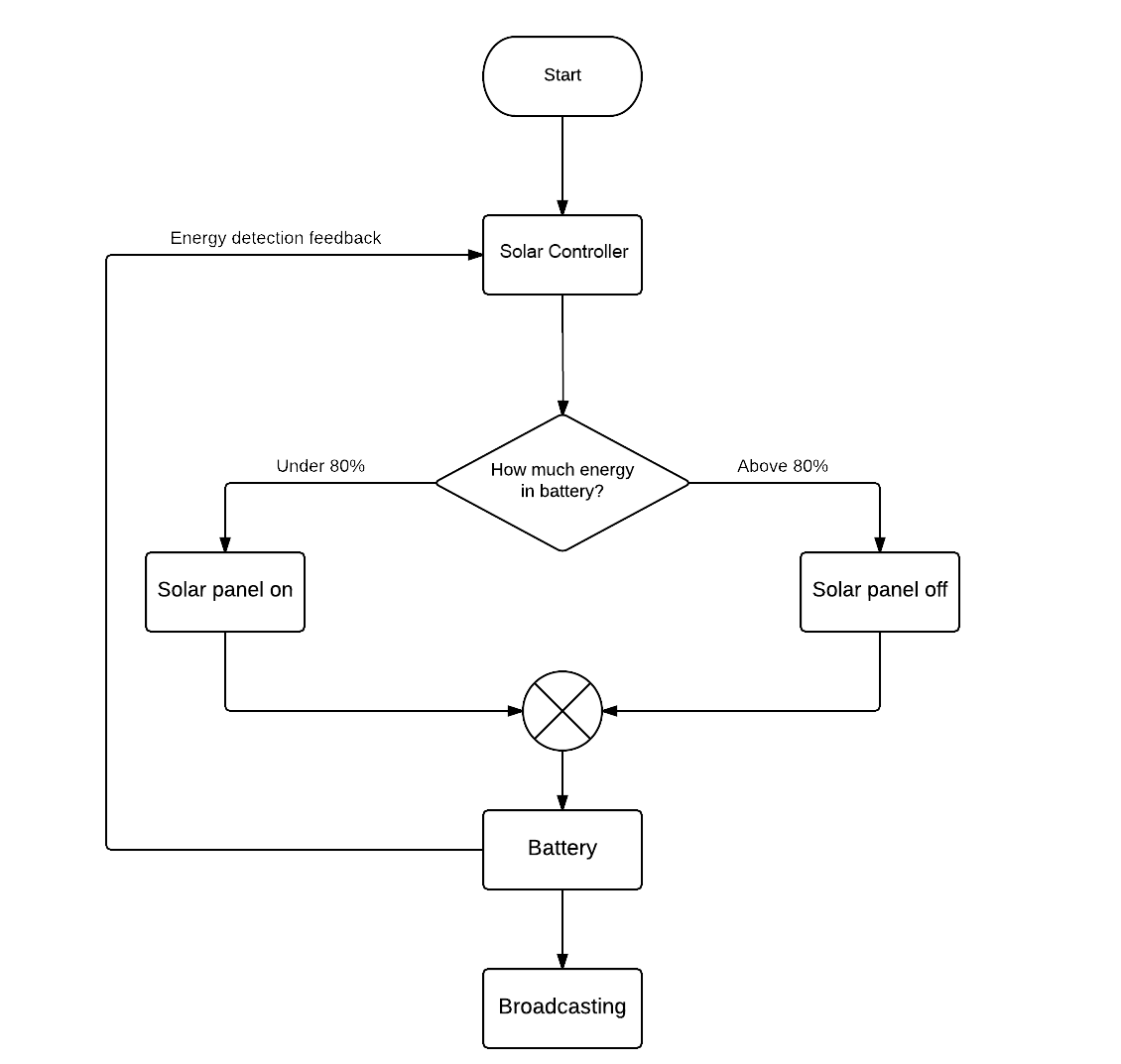
When the user initializes the device, the solar controller will automatically measure the power capacity of the battery. If the energy capacity is greater than the controller's factory default setting of power capacity, the system will automatically cut off the connection between the solar panel and the battery in case of overcharge hazard. Moreover, the controller will continuously record relevant parameters from the power sources to help achieve maximum operability of the device.
Solar Power Regulation
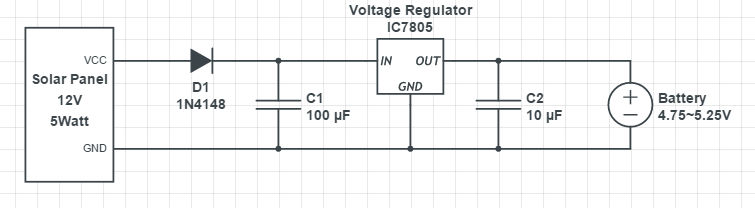
The circuit above is one possibility for a solar panel charging circuit. However, with the application of solar power, the battery can be continuously charged during daytime, by integrating the circuit into the device. With sufficient sunlight intensity, the output voltage of solar panel is 6V. Capacitors C1 and C2 act as current buffers in order to avoid interruption in current flow from the panel by affecting the charging process. Diode D1 is to regulate the current from solar panel. The voltage regulator IC7805 provides around 5 volts of voltage to battery.
Design Option
There are three design options for our design. The general idea is as same as the flow chart indicates. A solar power system continuously charges the rechargeable battery during daytime. Controller detects the power capacity of the battery and switches off the solar charging in order to prevent from overcharging battery when the capacity is above threshold value. The difference between the design options is the electronic components attached to the wood. The first design is to use the exciter to broadcast sound throughout wood instead of the tweeter in the second design. The third design is to use the tweeter and exciter at the same time to maximize the amplitude of sound. All of them are possible design options for our project. Moreover, the final outcome depends on experiments in next semester. The graphs below are the design drafts.