Remediation Alternative Analysis
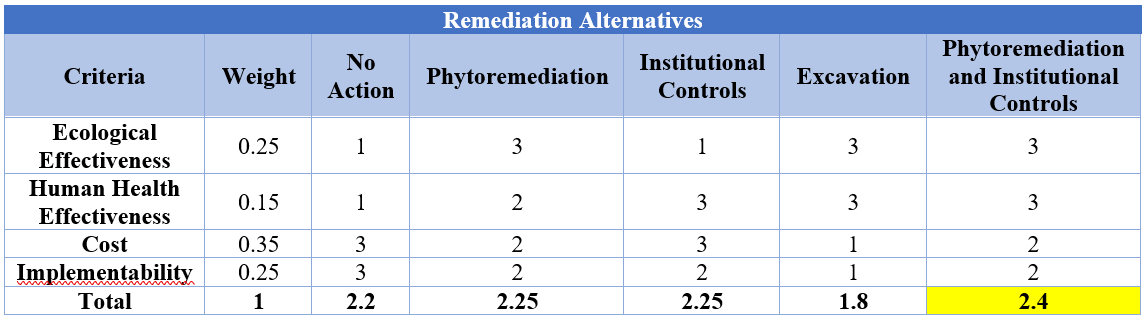
A decision matrix was constructed to determine what alternative was best for the site. Four different criteria were selected and used to analyze each alternative. The decision matrix constructed can be found in the table below:
Table 1: Decision Matrix
Alternative 5, a combination of phytoremediation and institutional controls, scored the highest. For phytoremediation, short grass species and sunflowers are recommended for the vegetation to be plated. According to the EPA, small plants like ferns and grasses are used in areas where soil contamination is shallow . Since contamination is predominantly at the surface, grass would be recommended. Deer grass is highly recommended for use because it requires low to moderate water, can endure large exposure to the sun, can live above 2,000 ft in elevation, and is native to Arizona. Yellow Pygmy Sunflowers are suggested due to their ability to withstand high amounts of arsenic. Josue A. Juarez, an alumnus of NAU conducted a research study that showed that not only were Yellow Pygmy Sunflowers able to absorb arsenic from the soil, but they were also found to be taller and healthier than sunflowers not exposed to arsenic . Sunflowers are also native to Arizona, can withstand high exposure to sunlight, need low to moderate water, and can survive in elevations above 2,000 ft. Fencing and signage will also be put around DU1. Signage will warn recreational visitors and inform the public of potential hazards on the site. Signage will also include information regarding the process of phytoremediation and the plants being used. Fencing will cover the perimeter of DU1 to prevent human and animal access.