Our Projects
On our campus and the surrounding roads, the degree of road damaging will be different every year. Traditionally, the department of transportation uses a huge detection car to detect road damage. Our client Dr. Ho finds that it was not only cumbersome, but also only applicable to motor vehicles, and it is expensive. Hence, the goal of our team is to finish the same function based on bikes. However, compared to the huge detection car, our devices have more advantages: it costs less, applies to any road, and is more portable.
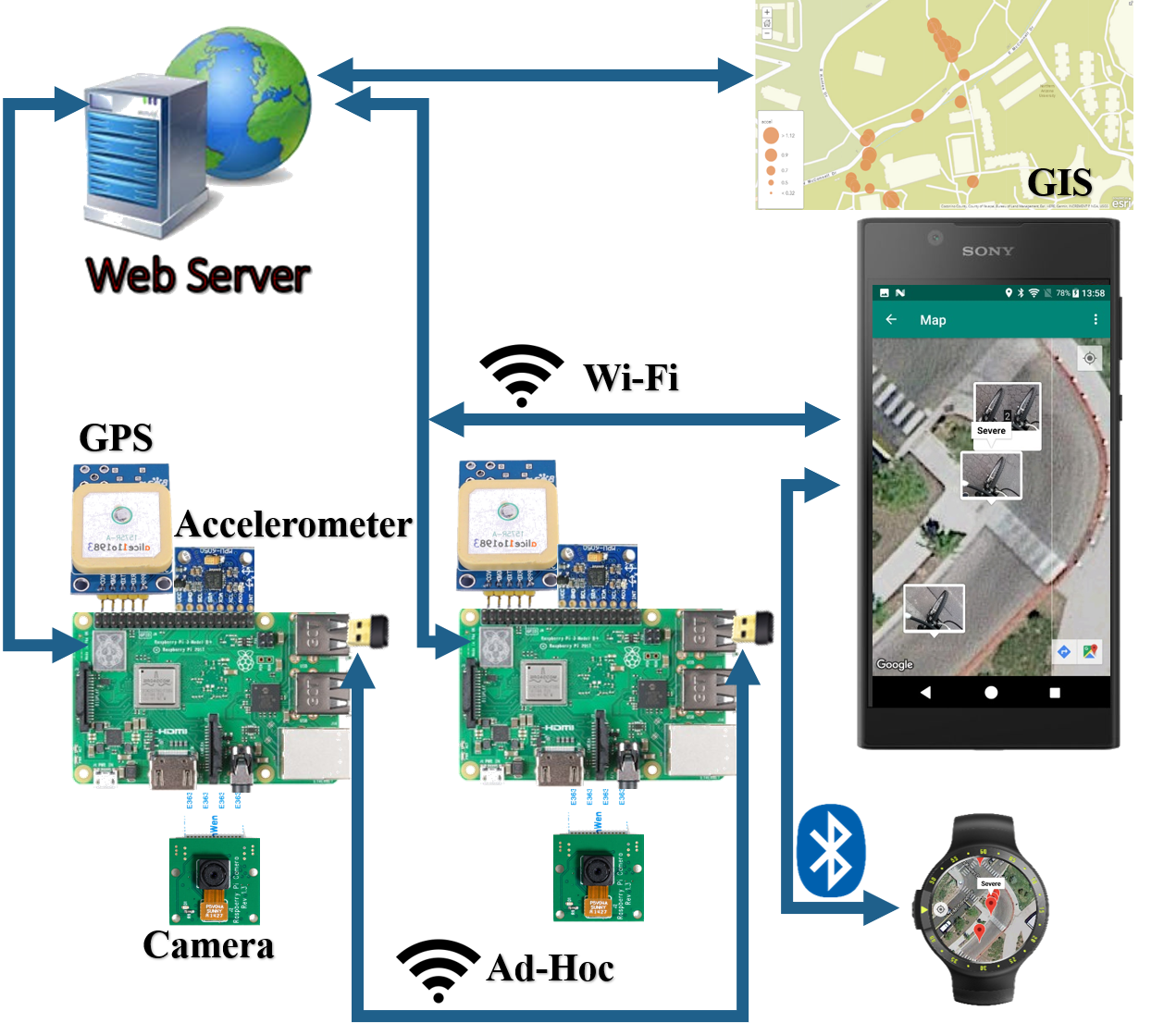
The basic components consist of a camera, an accelerometer, the Global Positioning System (GPS), the Android mobile application development, and data analysis. The accelerometers will save three-dimensional data, the camera will show real-time videos of the roads as a reference, and the GPS will record the location information of the bumps. As for the App, we determine to design one for the Android system with a humanized user interface.
In terms of the data sharing, we use Wi-Fi and wireless mesh network (WMN) to share the information with other users. Finally, our test routes mainly focus on bike lanes on campus, which helps us to amend our design scheme based on the results of each experiment.
Project Dipiction
Wireless communication
Communication between sensor and Raspberry Pi
Allowing smooth transition between Linux and Raspberry Pi
Data collection
Collecting sets of data for analyzation of dynamic threshold and terrain recognition algorithm.
Ex: Biking around campus based on weather conditions
Wet, Snow, Dry, etc.
Data processing
Process collected data from accelerometer and camera and provide feedback for users’ route plan decision making
Recognize the terrain’s type by images and machine learning algorithm.
Our Projects
hardware and software tools we used
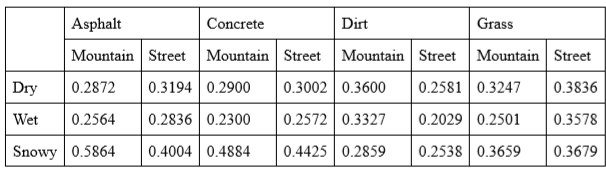
Test
Due to COVID 19 our test is mainly about the data we collectedhere is what we got from the test
you can see more detail abput our test in our paper which is in the final project